How to Choose the Right SDLC Model and Where QA Testing Fits in Each

Selecting the right software development life cycle (SDLC) model is one of the most important decisions a company makes when building a product. The right model helps teams deliver high-quality software on time, within budget, and with fewer surprises. The wrong model creates delays, miscommunication, technical debt, and ultimately, failed product launches.
Many startups and even established enterprises don’t fail because of technical weaknesses, but because of poor process planning. Teams jump into development without choosing the right SDLC structure, without defining quality checkpoints, or without aligning QA testing with the product’s complexity and release strategy.
This article will walk you through the most widely used SDLC models, explain how testing fits into each one, and show where crowd testing brings unique value regardless of methodology. You’ll also find a practical decision-making framework to help you choose the best SDLC model for your project, plus insights on how Ubertesters can strengthen quality assurance in every scenario.
What Is the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)?
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured framework that guides how software is planned, designed, developed, tested, deployed, and maintained. It ensures that teams follow a predictable and repeatable process, reducing risks and improving software quality at every stage.
Typical SDLC stages include:
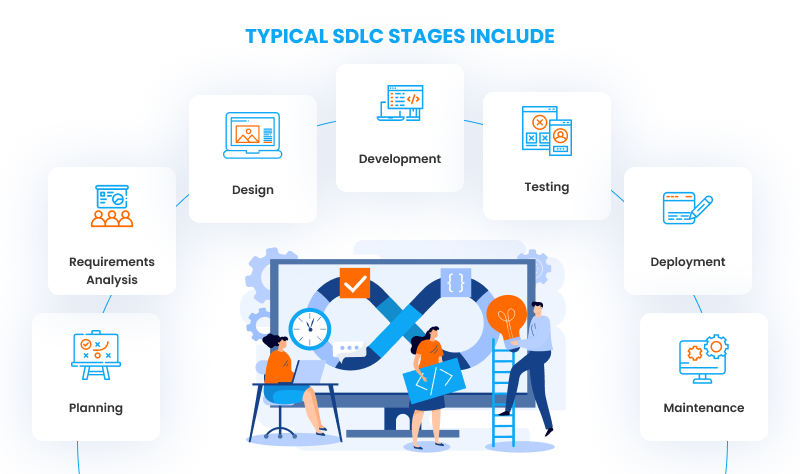
- Planning
Defining the project scope, goals, budget, risks, and team roles. - Requirements Analysis
Documenting functional and non-functional requirements and aligning expectations with stakeholders. - Design
Creating the architecture, UX/UI, technical specifications, and development blueprint. - Development
Writing the code, integrating components, and preparing builds. - Testing
Validating functionality, performance, usability, security, and compatibility. - Deployment
Releasing the product to production environments, app stores, or enterprise systems. - Maintenance
Monitoring performance, fixing bugs, releasing updates, and improving features.
Although “testing” is listed as its own stage, modern SDLC practices emphasize that QA is not a single step it should validate and support every other phase. Testing can begin during requirements, continue through development, and evolve long after launch.
Modern QA strategies typically combine:
- Manual testing (exploratory, functional, usability)
- Automated testing (CI/CD pipelines, regression, API testing)
- Crowd testing (real users across countries, devices, and environments)
Together, these methods give teams the coverage they need to ensure both functional quality and real-world reliability.
Overview of Key SDLC Models and Where QA & Crowd Testing Fit
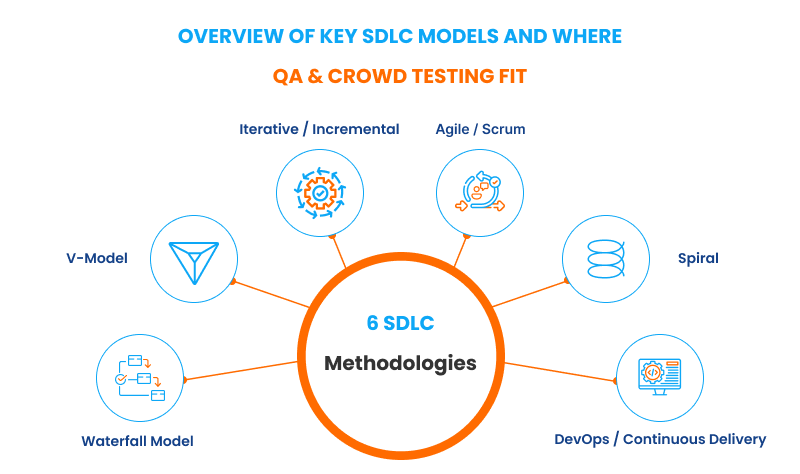
There is no single “perfect” SDLC model. Each one has strengths suited to specific project types, budgets, and organizational cultures.
Below is an overview of the most commonly used SDLC models:
- Waterfall
- V-Model
- Iterative / Incremental
- Agile / Scrum
- Spiral
- DevOps / Continuous Delivery
Let’s explore each, focusing on how QA testing, especially crowd testing, fits into the process.
1. Waterfall Model
The Waterfall model is the most traditional SDLC method, structured in strictly sequential phases. Each stage must be completed before the next begins, with minimal room for iteration or flexibility.
Best for:
- Projects with stable, well-defined requirements
- Regulatory or compliance-driven industries
- Enterprise systems with long release cycles
Where QA Testing Fits
Testing begins only after development is fully complete. This means:
- Requirements → no testing
- Design → no testing
- Development → no testing
- Testing happens only at the end
This significantly increases the risk of discovering defects late, when they are most expensive to fix.
Crowd Testing in Waterfall
Crowd testing plays a critical role, especially toward the end of Waterfall projects:
- Large-scale user acceptance testing (UAT)
- Device compatibility testing for global launches
- Localization testing for multilingual products
- Regression testing on a wide variety of platforms
- Pre-release validation before a major launch
Crowdsourced testers offer real environments, real network conditions, and diverse user behaviors, something an in-house team cannot replicate at scale.
2. V-Model (Verification and Validation)
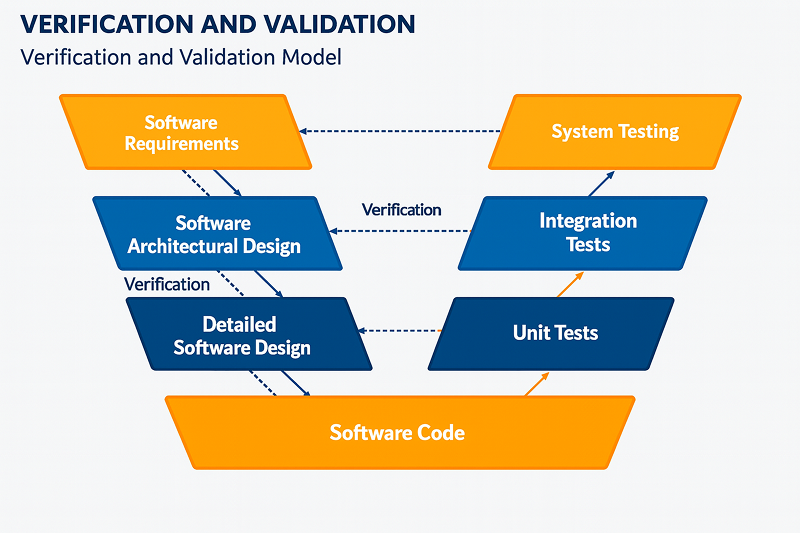
The V-Model is an extension of the Waterfall model, where each development phase has a corresponding testing phase planned in parallel. It is one of the most rigorous SDLC models.
Best for:
- Medical, automotive, military, and aerospace industries
- Highly regulated or safety-critical systems
- Projects requiring extensive documentation and traceability
Where QA Testing Fits
In the V-Model, QA is integrated into every step:
- Requirements → Acceptance test design
- Architecture → System test design
- Modules → Unit test design
This model ensures thorough verification at each stage before moving forward.
Crowd Testing in the V-Model
Crowd testing enhances the validation side of the V:
- Real-user feedback for usability and functionality in diverse environments
- Market-specific compliance checks, especially for fintech and healthcare
- Extensive pre-release validation across countries and platforms
- Localized regulatory testing
The diverse expertise of testers helps reveal edge cases that a controlled environment may overlook.
3. Iterative / Incremental Model
The iterative and incremental model builds the system through partial but functional releases. Each iteration includes planning, design, development, and testing.
Best for:
- Medium to large projects with evolving requirements
- Products requiring early user feedback
- Teams that require more structure than Agile, but more flexibility than Waterfall
Where QA Testing Fits
QA testing is performed at the end of each iteration:
- Each increment is tested individually
- Regression tests ensure compatibility with previous increments
- Feedback loops reduce technical debt early
Crowd Testing in Iterative Projects
Crowd testers help validate:
- Usability of each increment
- Cross-functionality across devices
- Real-world behavior as new modules integrate
- Feedback on early prototypes
The approach supports consistent user-centric validation at every release milestone.
4. Agile / Scrum Model
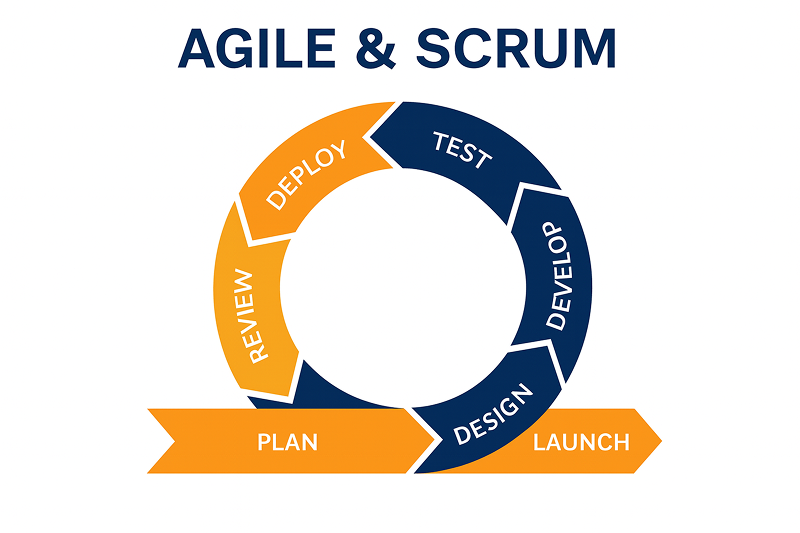
Agile is the most widely used SDLC model today, focused on collaboration, flexibility, and continuous delivery. Work is broken into 2–4 week sprints with iterative releases.
Best for:
- Startups and fast-moving scaleups
- Products with evolving requirements
- Teams prioritizing early and frequent user feedback
- Companies with continuous delivery
Where QA Testing Fits
QA is integrated into every sprint:
- Testers join during requirement refinement
- Testing happens alongside development
- Shift-left testing ensures early defect detection
Testing types include:
- Functional
- Exploratory
- Regression
- Usability
- API and integration testing
Crowd Testing in Agile
Crowd testing aligns naturally with Agile’s rapid cycles:
- In-sprint exploratory testing to uncover fresh insights
- Pre-release validation across platforms, devices, and networks
- Usability testing for new features before demos
- Continuous real-world feedback to shape user stories
Crowd testing offers speed, global scale, and variability essential for Agile’s fast cadence.
5. Spiral Model
The Spiral model combines design, prototyping, and risk analysis in iterative cycles (spirals). Each cycle includes four phases: planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation.
Best for:
- High-budget, complex, and high-risk projects
- Products that require extensive prototyping
- R&D-heavy software initiatives
Where QA Testing Fits
Testing is performed at the end of each spiral:
- Validates whether risks identified earlier were resolved
- Ensures each prototype meets key requirements
- Prepares the product for the next cycle
Crowd Testing in Spiral
Crowd testing supports early and ongoing validation:
- Prototype testing with real users
- Risk identification in real environments
- Market validation across geographies
- Beta testing with actual customers
The diversity and scale of testers help organizations identify issues early and refine prototypes faster.
6. DevOps / Continuous Delivery Model
DevOps unifies development and operations to deliver rapid, frequent updates with continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD).
Best for:
- SaaS products
- Platforms with daily or weekly updates
- Teams with strong automation maturity
- Companies prioritizing high uptime and fast innovation
Where QA Testing Fits
Testing is continuous and automated:
- Integrated into CI pipelines
- Automated regression suites
- Automated unit, integration, and smoke tests
- Monitoring and QA in production
QA works alongside development, operations, security, and monitoring teams.
Crowd Testing in DevOps
Crowd testing enriches DevOps pipelines with:
- Continuous real-world validation in staging
- Smoke testing on real devices before deployments
- Post-deployment monitoring by humans
- Exploratory testing for newly released features
- Load and performance validation at scale
Crowd testing introduces broad device, country, and network coverage essential for DevOps speed.
How to Choose Your SDLC Model (Decision Framework)
Choosing the right SDLC model depends on several factors that relate to your product, team, timelines, and risk tolerance.
1. Project Size & Complexity
- Small or simple → Waterfall / Iterative
- Large, complex, evolving → Agile / Spiral / DevOps
2. Requirement Stability
- Fixed and clear → Waterfall / V-Model
- Changing or uncertain → Agile / DevOps
3. Customer Involvement
- Low involvement → Waterfall
- High involvement → Agile / Iterative
4. Time-to-Market
- Long-term release → Waterfall / V-Model
- Fast releases → Agile / DevOps
5. Team Structure & Culture
- Co-located, formal → Waterfall / V-Model
- Distributed, collaborative → Agile / DevOps
6. Risk Tolerance
- High risk analysis required → Spiral
- Continuous feedback for risk mitigation → Agile / DevOps
Key Insight:
There is no universally superior SDLC model. The goal is to choose one that maximizes efficiency, quality, and adaptability for your specific needs. Your QA strategy must evolve with your SDLC model, not the other way around.
The Benefits of Ubertesters in the SDLC
Regardless of which SDLC model your team uses, one thing remains constant: real-world validation is essential for high-quality software. This is where Ubertesters becomes a powerful partner.
1. Unmatched Global Coverage
Test with real people in 150+ countries, across countless devices, languages, operating systems, and network conditions.
2. Fast, On-Demand Testing
Access a flexible pool of testers who can begin validating your product within hours, perfectly supporting Agile, Spiral, and DevOps timelines.
3. End-to-End Test Management
Ubertesters provides:
- Professional test leads
- Test planning and execution
- Dashboards and live bug reporting
- Complex test scenarios
This ensures structure and consistency across all SDLC models.
4. Comprehensive Real-User Feedback
Receive insights not only on functionality, but on:
- Usability
- Performance
- Localization
- Security considerations
- Payment testing
- Device-specific issues
5. Cost-Effective Scalability
Scale testing coverage as needed without increasing fixed QA costs. Ideal for:
- Agile teams with fluctuating workloads
- DevOps teams with frequent releases
- Enterprises conducting large UAT cycles
6. Integration Ready
Ubertesters integrates with:
- CI/CD systems
- Jira
- TestRail
- Other test management tools
This makes it easy to embed crowd testing into any SDLC.
Ubertesters is the indispensable partner for real-world quality, no matter what SDLC model you choose.
Conclusion
The SDLC model you choose becomes the backbone of your software project. Whether you follow Waterfall, Agile, Spiral, or DevOps, each model demands a different approach to quality assurance.
But one principle remains universal:
Robust QA, especially with the flexibility of crowd testing, is the foundation of successful software development.
Crowd testing ensures that your SDLC is not only structured and efficient, but also grounded in real-world user behavior across devices, languages, and environments.
Don’t let the wrong SDLC model slow your product down. Reach out to our experts and ensure flawless QA integration at every stage of development today.

